DIOVC
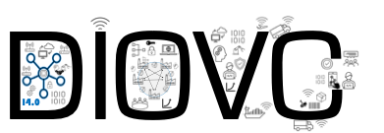
The conceptual model for the DIOVC maturity model is based on the main elements related to interorganizational value chains. The capabilities includes four dimensions with 18 capabilities that supports organizations to improve the value chain performance.
Digital Inter-organizational Value Chain Maturity Model and Assessment Tool
Our DIOVC assessment tool for precise evaluation and improvement of digital Industry 4.0 innovation capabilities in value chains.
Approach
Our DIOVC Maturity Model Assessment Tool evaluates your current status, helping organizations identify gaps and potential opportunities. This enables you to enhance both individual and overall maturity levels by developing tailored digital innovation roadmaps within your organizationa and accross your key customers/suppliers.
Status
The BETA-Version of our DIOVC Assessment tool is ready for Model Deployment and Application for product evaluation in potential case manufacturing organizations.
Benefits
Driving Effective and Efficient Value Chains for Organizational Success
Our strategic roadmap cultivates value chains that are both effective and efficient, paving the way for enhanced organizational success through increased revenue and operational excellence. By minimizing the risk of the productivity paradox, we ensure that your business thrives in today’s competitive landscape.
Dimension "Digitalization"
aligns digital innovation initiatives with value chain objectives and adopts methodology to realize the untapped potential of resources across interorganizational entities. This covers six capabilities:

Digitalization Strategy
formulates a boundary-spanning direction and aligns its implementations. Digital innovations allow to access/share resources across IOEs to meet common goals of joint breakthrough objectives.

Digitalization Culture and Resources Development
develops cognitive readiness of entire organizations towards “digital values” that rely on collaboration, learning, trust, commitment, and shared meanings out of interorganizational relationships. IOEs develop their human resources digital competencies.

Digital Operations
enable real-time collaboration between workforces of IOEs through the interoperability of digital technologies; the management of operational resources, systems, and bots; and adjustment of aligned capacities to make better decisions about improving the performance of digitalized value chains.

Digital Products and Services
progressively create, deliver, and capture increased product and service values from a broad range of enabling digital technologies. Organizations sense novel opportunities that comprise business model updates out of end-to-end data management across organizations.

Digital Total Experience
explores a full understanding of the involved stakeholders, their behaviors, requirements, and expectations based on the relevant and available information. Identifies opportunities for top-line growth and influences the relationship out of stakeholder touchpoints.

Digital Business Process Orientation
exceed the intra-organizational BPM perspective and coordinate across IOEs to agree already in the early BPM modeling phase for low maturity levels the interorganizational end-to-end BP requirements with cross-organizational performance measures, and a interconnect between the BPM and IOE control management related security, compliance, and BPM governance mechanism.
Dimension "Technology Implementation"
execute the digitalized innovation efforts by implementing technological changes to interorganizational business processes.

Technology Enablers
coordinates the joint technology roadmap towards a digital value chain across IOEs, enabling technology implementation and integration to meet the common objectives.
Program Management System
coordinates all aligned milestones and tasks on IOE level. PMS monitors and evaluates which capabilities and resources need to be acquired by whom and when during the implementation period to meet the joint program and individual project milestones.

Human-Machine Relationship
covers the aligned adaptation of users and technologies as a priority by joint user training. It ensures human-machine interactions and collaboration (automation and autonomy) in a virtual/digital world.

Technology Infrastructure
coordinates the infrastructure specification during the implementation process across IOEs, and defines the technological requirements and priorities to align the subsequent needed investments and resources with transforming into a digital value chain.
Supply Chain Management
redesigns the current value chain by understanding how complex design topics affect the interactions among various components (flows of material, information, and finance) to jointly reach the various steps in the digital value chain transformation.

SCM Integration
describes different levels of information sharing (collaborative planning, forecasting, and replenishment), resource sharing (decision delegation, work realignment, outsourcing), and organizational relationship linkage (extended communication and performance measures, incentive realignment) out of integrated business processes across IOEs.

Ambidextrous SCM reconfiguration
utilizes simultaneous the ability to maintain daily operations excellence while looking for constant innovation. Organizations are capable of changing the structural boundaries across IOEs and reconfiguring SCM components permanently by adding to, deleting from, or moving within the organizations and/or across IOEs.

SCM Automation
delivers real-time responsiveness and agility in value chains, created as an outcome of effective usage of aligned robotic technology in process automation and by joint modeling of intelligent business processes.

SCM Analytics
full utilized interpretations of end-to-end data in value chains and real-time execution decisions of the affected IOEs, with joined efforts of value chain optimization by process analytics (descriptive and prescriptive), advanced planning, and predictions.
Interorganizational Relationship (IOR)
covers the relationships between IOEs that enable and manage digital transactions, flows, and linkages between organizations.

IOR Governance
supervises the content flows and objectives alignment, and manages the relationships (trustworthiness, incentive structures, reciprocity, and equity) with rules of digital and conventional exchange between partners and their IOE governance bodies (steering committee, program office.

IOR Content
coordinates the resource-sharing decisions across IOEs, and manages the resource and information flows, their intensity, and frequencies by allocating tasks, responsibilities, resources, and knowledge.

IOR Structure
defines structural attributes, linkages (quality of ties) for diverse types of relationships, and structural variables (formalization, density, intensity, centrality, and stability) that affect the organizational willingness to cooperate (10). It implies a permanent, structural reconfiguration and selection of diverse partners that are motivated to invest in/share resources.

Multi-Enterprise Architecture
specifies the collaborative design, implementation, evolution, and management related to IS and security of IOE infrastructure. It is a pre-requisite for transparent and secure inter-organizational information exchange and horizontal business processes determined by four layers (business, information, application, and technology.
©KAIKU Nottbrock Consulting. All rights reserved.
Wir benötigen Ihre Zustimmung zum Laden der Übersetzungen
Wir nutzen einen Drittanbieter-Service, um den Inhalt der Website zu übersetzen, der möglicherweise Daten über Ihre Aktivitäten sammelt. Bitte überprüfen Sie die Details in der Datenschutzerklärung und akzeptieren Sie den Dienst, um die Übersetzungen zu sehen.